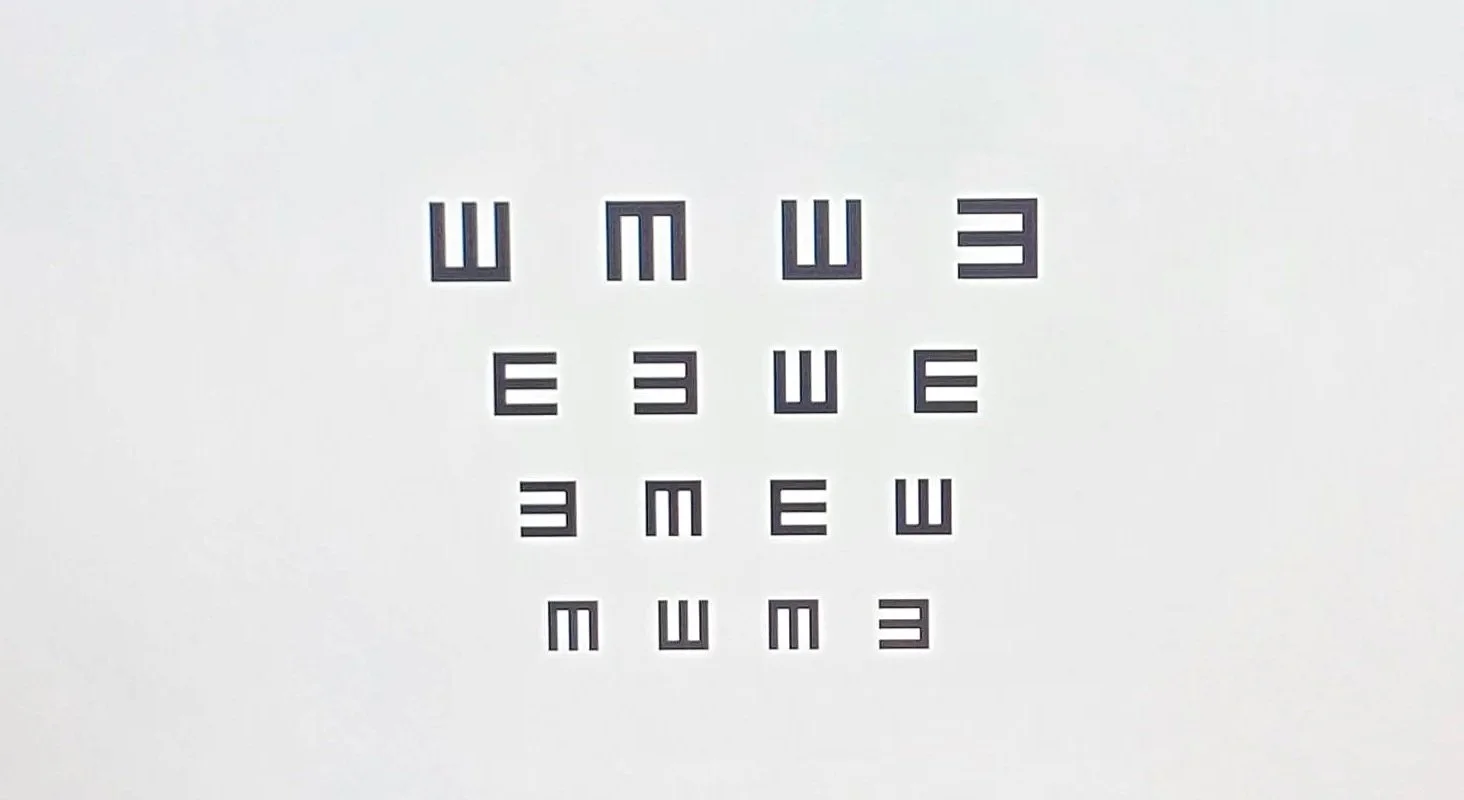
Comprehensive eye exams
Comprehensive eye exams by a doctor of optometry are an important part of caring for your eyes, vision, and overall all health.
Periodic eye and vision examinations are an important part of preventive health care. Many eye and vision problems have no obvious signs or symptoms, so you might not know a problem exists. Early diagnosis and treatment of eye and vision problems can help prevent vision loss. Each patient's signs and symptoms, along with your doctor of optometry's professional judgment, will determine what tests are conducted. A comprehensive adult eye and vision examination may include but is not limited to, the following tests.
Patient history
The doctor will ask about any eye or vision problems you are currently having and about your overall health. In addition, a patient history will include when your eye or vision symptoms began, medications you are taking, and any work-related or environmental conditions that may be affecting your vision. The doctor will also ask about any previous eye or health conditions you and your family members have experienced.
Visual acuity
Visual acuity measurements evaluate how clearly each eye is seeing. Reading charts are often used to measure visual acuity. As part of the testing, you will read letters on charts at a distance and near.
The results of visual acuity testing are written as a fraction, such as 20/40. The top number in the fraction is the standard distance at which testing is done (20 feet). The bottom number is the smallest letter size you were able to read. A person with 20/40 visual acuity would have to get within 20 feet to see a letter that should be seen clearly at 40 feet. Normal distance visual acuity is 20/20.
Preliminary tests
A doctor of optometry may first want to look at specific aspects of the patient's visual function and eye health. Preliminary tests can include evaluations of depth perception, color vision, eye muscle movements, peripheral or side vision, and the way your pupils respond to light.
Keratometry/topography
These tests measure the curvature of the cornea (the clear outer surface of the eye) by focusing a circle of light on the cornea and measuring its reflection. This measurement is particularly critical in determining the proper fit for contact lenses.
Refraction
Refraction determines the lens power needed to compensate for any refractive error (nearsightedness, farsightedness or astigmatism). Using an instrument called a phoropter, the doctor places a series of lenses in front of your eyes. He or she then measures how these lenses focus light using a handheld lighted instrument called a retinoscope. The doctor may choose to use an instrument that automatically evaluates the focusing power of the eye. The lens power is then refined based on the patient's input on the lenses that give you the clearest vision.
This testing can be done without eye drops to determine how the eyes respond under normal seeing conditions. However, a doctor of optometry will use eye drops with patients who can't respond verbally or when some of the eyes' focusing power may be hidden. The drops temporarily keep the eyes from changing focus during testing.
Eye focusing, eye teaming, and eye movement testing
To see a clear, single image, the eyes must effectively change focus, move and work in unison. An assessment of accommodation, ocular motility, and binocular vision determines how well your eyes focus, move and work together. This testing will look for problems that keep eyes from focusing effectively or make using both eyes together difficult.
Eye health evaluation
A wide variety of microscopes, lenses, and digital technology will be used to assess the health of all the structures of the eye and the surrounding tissues. Dilating eye drops are often used to temporarily widen the pupil for better views of the structures inside the eye. In addition to measuring the pressure inside of the eye, this also is part of the eye exam where a doctor of optometry can detect otherwise unknown eye and systemic diseases.
Supplemental testing
Additional testing may be needed based on the results of the previous tests to confirm or rule out possible problems, to clarify uncertain findings, or to provide a more in-depth assessment.
At the completion of the examination, the doctor will assess and evaluate the results of the testing to determine a diagnosis and develop a treatment plan. He or she will discuss with you the nature of any visual or eye health problems found and explain available treatment options. In some cases, referral for consultation with, or treatment by, another doctor of optometry or other health care provider may be indicated. If you have questions about any diagnosed eye or vision conditions, or treatment recommendations, don't hesitate to ask your doctor for additional information or explanation.
Patients at risk include those:
A personal or family history of ocular disease.
Belonging to certain racial and ethnic groups.
Systemic health conditions with potential ocular manifestations.
Occupations that are highly demanding visually or have a high potential of being hazardous to the eyes.
Taking prescription or nonprescription drugs with ocular side effects.
Functional vision in only one eye.
Wearing contact lenses.
Eye surgery or previous eye injury.
High or progressive refractive error.
Other eye-related health concerns or conditions.
Patients who have undergone refractive surgery (LASIK, PRK, SMILE) should still have an eye exam every 1-2 years for monitoring of overall ocular health.
